Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-24 Origin: Site








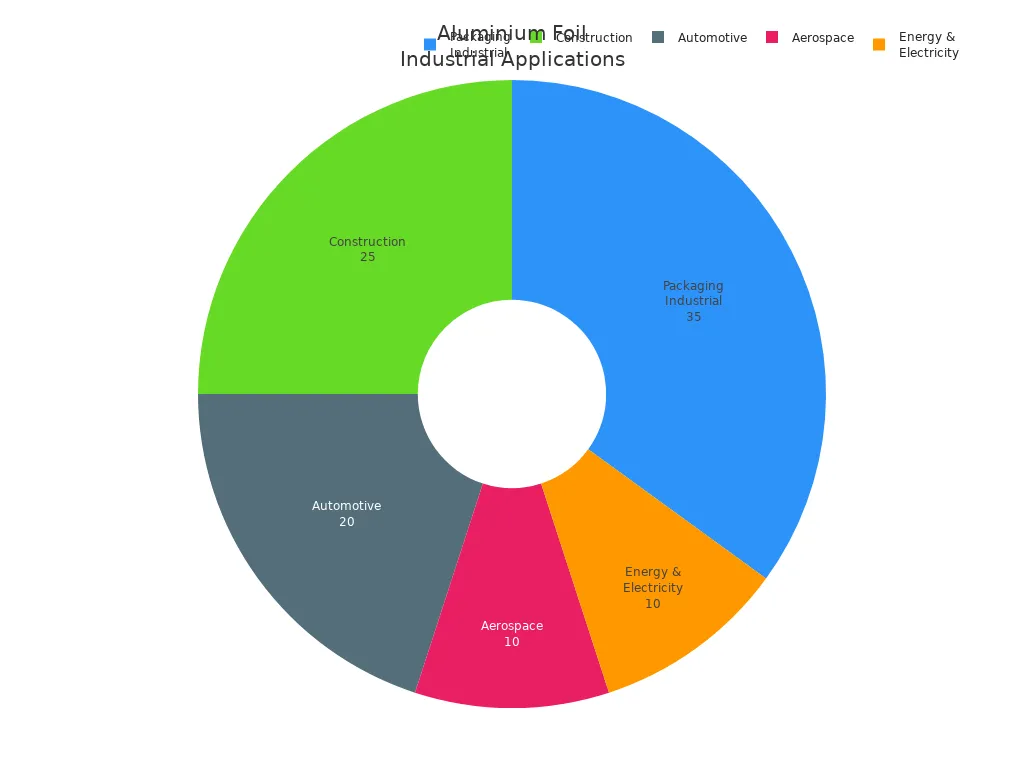
Aluminum foil begins as bauxite. Bauxite is turned into alumina. Then, it becomes pure aluminum by smelting. Workers cast and roll the aluminum into thin sheets. Machines and special production lines help make the foil. BOWAY’s foil container line and rewinding machine are examples. These machines help make the foil even and high-quality. Strong quality control checks every batch. This makes sure it meets industry rules. Aluminum foil has many uses. It is used a lot in food, packaging, and machines. The world market for aluminum foil was $30.17 billion in 2024. The market is still growing. Food and drink packaging uses more than 41% of all aluminum foil.
Aluminum foil comes from bauxite ore. The ore is mined first. Then it goes through refining, smelting, casting, and rolling. These steps make thin and strong sheets.
Modern machines help make better foil. Automation, like BOWAY’s equipment, keeps the foil the same thickness. It also helps stop mistakes during making.
Aluminum foil keeps food safe. It blocks water, air, and germs. This helps food stay fresh and safe when stored or cooked.
Quality checks happen at every step. They check from raw materials to finished foil. This makes sure the foil is safe and meets high standards.
Handle foil the right way to keep it clean. Pick foil with food safety labels. This helps keep it safe to use. Recycling aluminum foil saves energy. It also helps the environment.
Aluminum foil starts deep underground as bauxite. It ends up as a shiny, bendable sheet. People use it at home and in factories. Making aluminum foil takes many steps. Each step uses new machines and careful checks. Factories like BOWAY use special machines and robots. These help make the process fast and the foil the same every time.
Aluminum comes from bauxite ore. Miners dig it out of the ground. Australia, China, Guinea, Brazil, and India mine the most bauxite.
Country | Annual Bauxite Output (million metric tons) | Additional Context |
|---|---|---|
Australia | 105 | Leading producer with strong mining infrastructure and export systems. |
China | 68 - 90 | Second largest producer; imports from Guinea, Australia, Indonesia. |
Guinea | 64 - 86 | Third largest; holds the world's largest bauxite reserves. |
Brazil | 30 - 33 | Major mines in Pará state. |
India | 26 | Odisha state is the main producing region. |
Mining bauxite can hurt nature. It can destroy animal homes and pollute water and air. Good companies try to follow rules to protect the environment.
After mining, workers turn bauxite into alumina. They use the Bayer process. This process has a few steps:
Workers crush bauxite and mix it with sodium hydroxide. They heat it up under pressure.
The mix dissolves aluminum parts and leaves waste behind.
When the mix cools, aluminum hydroxide crystals form.
Heating these crystals at 1200°C makes alumina.
This white powder is needed for the next step.
Next, alumina goes through the Hall-Héroult process. Workers put alumina in melted cryolite inside a steel pot. They run electricity through it. Aluminum splits from oxygen and sinks to the bottom. This is how most aluminum is made today.
Note: The Hall-Héroult process uses lots of energy. Recycling aluminum saves almost all of this energy.
Now, the aluminum is ready for casting and rolling. Workers pour melted aluminum into big blocks. These blocks are rolled to make them thinner.
Melting and casting: Aluminum is melted and shaped into blocks.
Homogenization: The blocks are heated to make them better.
Hot rolling: The blocks are rolled while hot to get thinner.
Cold rolling: Rolling at cooler temperatures makes them even thinner.
Intermediate annealing: Heating between rolls makes the metal softer.
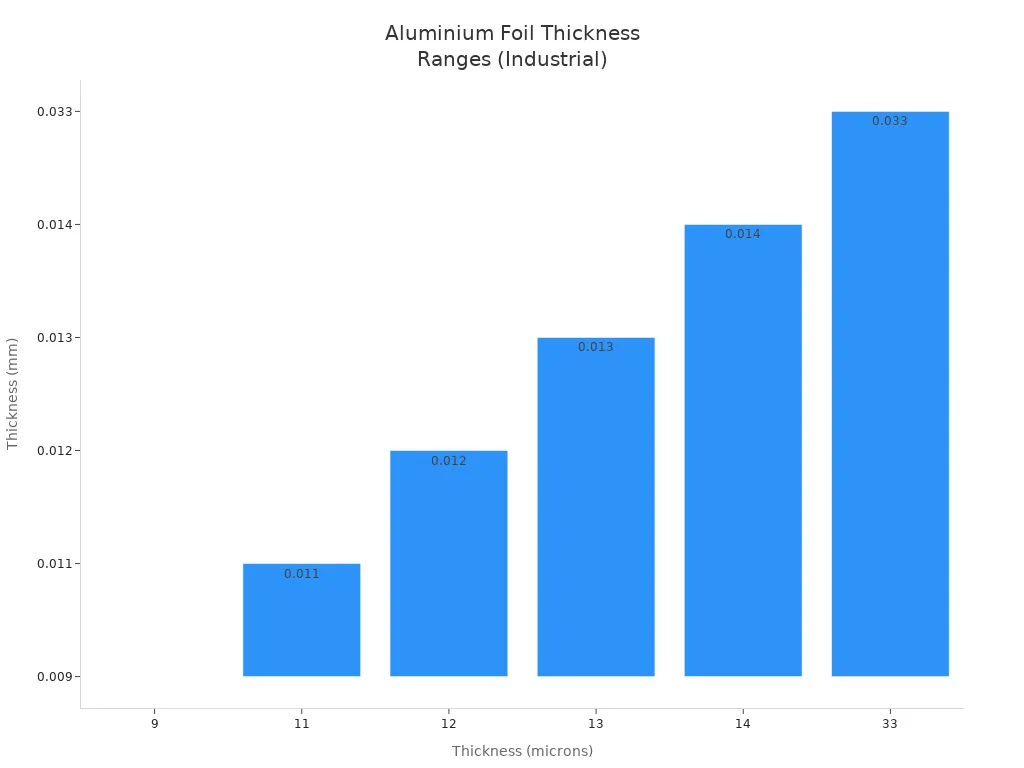
Final rolling: The aluminum gets as thin as foil, about 7 microns.
Modern machines, like BOWAY’s, use robots to check thickness and quality. These machines can make more foil and fewer mistakes. This helps every roll meet tough rules.
Efficiency Metric | Improvement Percentage | Description |
|---|---|---|
Production Rate Increase | Up to 40% | Automation boosts production rates by automating repetitive tasks, increasing output. |
Cycle Time Reduction | Approximately 30% | Automated processes reduce cycle times, enabling faster turnaround and higher throughput. |
Throughput Enhancement | 35% | Automated rolling and extrusion lines increase throughput by streamlining production flow. |
The last steps get the aluminum foil ready to use. These steps are:
Annealing: Heating the foil to make it softer and smoother.
Slitting and rewinding: Cutting the foil to the right size and rolling it up. Machines like BOWAY’s make sure cuts are neat and rolls are smooth.
Surface treatments: Adding layers for extra strength or heat protection.
Printing and embossing: Putting on designs, logos, or words.
Packaging: Wrapping and boxing the foil for shipping.
Finishing Process Category | Specific Processes and Treatments | Purpose/Effect |
|---|---|---|
Surface Treatment | Chromate-free passivation | Improves laminate adhesion |
Lamination | Extrusion lamination (PE, PET, OPP), Solvent lamination (EVOH) | Enhances bond strength and oxygen barrier |
Printing and Surface Finishing | Flexographic or gravure printing with UV-curable or solvent-based inks | High-resolution graphics, food/pharma safe |
Slitting and Rewinding | Precision slitting to widths (200mm to 1200mm) with tight tolerances (<±0.3 mm) | Ensures uniform bag sizes and smooth high-speed packaging |
Mechanical Strength | Use of thicker foil gauges (12–20 µm) with oriented PET/OPP layers | Provides puncture resistance and flexibility |
Aesthetic Finishes | Matte, gloss, soft touch lamination; embossing and debossing | Enhances tactile appeal and brand differentiation |
Surface Coatings | Anti-fog coatings, heat-seal coatings (PE, EVA), slip and anti-static agents | Maintains visibility, sealability, and processability |
Customization | Gusseted bottoms, zip closures, tear notches, laser scoring, special shapes | Adds functionality like reclosability, easy opening, and display features |
Tip: Annealing and slitting make the foil soft and easy to use. Doing these steps right stops problems and keeps the foil high-quality.
From bauxite to finished foil, the whole process uses smart machines and careful checks. Automation helps companies like BOWAY make strong, safe aluminum foil for food, factories, and machines.
Aluminum foil is special because of its physical and chemical properties. These features make it very useful in many industries. It is used a lot for food packaging and in machines. The table below lists the main properties of aluminum foil and why they are important:
Property/Characteristic | Description | Industrial Relevance/Use |
|---|---|---|
Aluminum Content | Over 99.35% in common alloys like 1235 and 1145 | Ensures purity and keeps aluminum’s best qualities |
Malleability and Formability | Easy to shape and roll into thin sheets | Allows production of smooth, thin aluminum foil |
Corrosion Resistance | Forms a thin oxide layer that protects against rust | Increases durability and keeps products safe |
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity | Transfers heat and electricity well | Useful for cooking, heat exchange, and electronics |
Lightweight | Low density metal | Makes packaging and parts easy to handle and ship |
Alloying Elements | Small amounts of other metals keep aluminum strong and workable | Customizes strength for different uses |
Strength and Hardness | Can be improved by cold-pressing or adding other metals | Meets special industrial needs |
Aluminum foil works as a strong barrier. It stops water, air, light, and germs from getting in. This helps food stay fresh and safe. Its thick structure protects better than plastic wraps or metallized films. Aluminum foil is safe and does not react with food, even when it gets hot.
Note: Aluminum foil can be recycled. Recycling uses much less energy than making new aluminum. This helps the environment and supports a circular economy.
Aluminum foil is used in many ways at home and in factories. Its special properties make it great for packaging, cooking, and making things. Here are some of the most common uses:
Food packaging for cheese, butter, baked goods, snacks, and ready-to-eat meals
Wrapping meat, fish, and leftovers to keep them fresh and stop spoilage
Making containers and trays with foil container production lines for takeout, baking, and airline meals
Lining ovens and grills to make cleaning easier and help heat spread evenly
Used in rewinding machines to make rolls for homes and factories
Protecting medicines, cosmetics, and sensitive products from light, water, and air
Used as insulation in buildings and in heat exchangers for air conditioners
Used in automation equipment for parts, housings, and shielding
Aluminum foil is light, bendable, and easy to shape. It helps lower shipping costs and saves energy. Because it can be recycled, it is a smart choice for companies that care about the planet. BOWAY’s modern production lines and quality checks make sure every roll of aluminum foil is safe and works well.
Quality control is very important in making aluminum foil. Companies use strict rules to make sure every roll is good. They check the foil at each step, from picking materials to the finished product. Factories use new technology like lasers and machines to check the foil. BOWAY uses robots, real-time checks, and works with customers. This makes sure every foil roll works the same, whether for a rewinding machine or a foil container line.
The first step is checking the raw materials. Workers look at the aluminum’s physical and chemical properties. They use special tools to check what metals are in the alloy and how pure it is. This stops bad things like titanium diborides or magnesium oxides from getting in. If these get in, they can cause holes or breaks in the foil. The table below lists tests done during raw material checks:
Test Type | Description |
|---|---|
Material Testing | Checks physical characteristics, chemical composition, and purity of aluminum. |
Thickness Measurement | Monitors foil thickness to ensure uniformity and compliance with standards. |
Strength Testing | Measures tensile strength and elongation for durability. |
Barrier Testing | Evaluates resistance to moisture, light, and oxygen for food safety and quality. |
Cleaning machines and the work area helps stop dirt from getting in. Picking the right aluminum and keeping things clean helps make good foil.
During production, teams watch every step closely. Machines check the thickness of the foil with lasers. Other tools look for problems like chips, scars, or bent edges. Real-time checks help fix problems fast. Some common problems found are:
Pinholes from dust or bad aluminum.
Scars from rubbing or wrong tension.
Wrinkles and bent edges from rolling mistakes.
Oil or water spots from dirty machines or handling.
Thickness changes from process issues.
BOWAY does more than most companies. They start with a meeting to learn what the customer needs. Engineers use 3D models to plan carefully. Special machines and presses make sure the foil is made right. They test each batch with the customer’s materials to check it meets the right standards. This teamwork and custom work make BOWAY different from others.
Tip: Checking quality at every step stops problems and makes sure the foil is good for food, machines, and other uses.
Aluminum foil helps keep food safe. Companies must follow strict rules to make sure foil does not hurt people. The table below lists important safety points for aluminum foil in food packaging:
Food Safety Standard Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Purity | Aluminum must be at least 99.5% pure to minimize contaminants and ensure safety. |
Non-Toxic Coatings | Coatings must be approved by regulatory bodies like the FDA to prevent harmful reactions with food. |
Regulatory Compliance | Must comply with FDA CFR Title 21 (USA) and EU Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004, among others. |
Corrosion Resistance | Aluminum forms a natural oxide layer to resist corrosion and maintain food safety. |
Prevention of Leaching | Engineered to prevent aluminum ions from leaching into food, especially acidic foods. |
Temperature Resistance | Must maintain integrity and safety under a wide range of temperatures, from freezing to high heat. |
Certifications | ISO 22000 and FDA approval are key certifications indicating compliance with food safety standards. |
Manufacturer Quality Assurance | Selecting reputable manufacturers ensures adherence to safety and quality standards. |
Aluminum foil stops water, air, and germs from getting in. This keeps food fresh and safe to eat. The foil stays strong in hot ovens and cold freezers. It works well for baking and freezing food. Be careful with foods like tomatoes or lemons. These can cause aluminum to get into the food. Using parchment paper inside the foil helps stop this. Buying foil from trusted brands like BOWAY is safer. These brands follow food safety rules. Always seal food well and do not store salty or sour foods in foil for a long time.
Tip: Look for FDA or ISO 22000 labels when buying foil for food.
Handling aluminum foil the right way keeps it safe and clean. People should do these things to stop damage or dirt:
Store foil rolls in a clean, dry place with good temperature. Keep them away from dust, water, grease, and strong smells.
Keep foil in its package or seal it tight after opening. This protects the foil from getting bent or dirty.
Handle foil gently. Try not to bend, crease, or tear it.
Keep foil away from sharp things and rough places to stop holes.
Use older foil rolls before new ones. This keeps the foil fresh.
Do not put foil in sunlight or very hot or cold places. This keeps it in good shape.
Keep the storage and work area clean. This is extra important for foil used with food.
BOWAY’s machines help keep foil clean and cut it just right. These machines lower the chance of dirt and make sure the foil is rolled well. Clean rooms and neat work areas also help protect the foil. Following these tips helps people get the best use from aluminum foil, for food or machines.
Note: Always check foil for damage before using it. Damaged foil may not protect food and could be unsafe.
Making aluminum foil starts with bauxite. It ends with careful finishing and strict checks. These steps make sure the foil is strong and safe. The foil works well at home and in factories. Aluminum foil keeps food safe and fresh. It also helps machines work better and saves energy.
Picking good aluminum foil is important. You should look for:
Foil that is always the same thickness and strength
Food safety labels like FDA or ISO
Sizes that fit what you need
Foil that is good for the planet and can be recycled
Brands you trust that use new machines, like BOWAY’s foil container line and rewinding machine
New ideas, like smart coatings and recycling, make foil work better and help the earth.
Bauxite is the main material for making aluminum foil. Workers dig bauxite out of the ground. Factories turn it into alumina, then pure aluminum. This makes strong foil for packaging and machines.
BOWAY uses modern machines and strict checks. Teams look at raw materials and watch every step. They also check the finished foil. Machines like the rewinding machine help keep the foil even and smooth.
Yes, you can recycle aluminum foil. Recycling saves energy and cuts down on trash. Many companies use recycled foil for food and factories. BOWAY helps the planet by using smart ways to make foil and by supporting recycling.
Aluminum foil is used in machines as a shield, for insulation, or as a cover. Factories use foil container lines and cartoning machines. These make packages for food, electronics, and machine parts.
BOWAY has new machines like foil container lines and rewinding machines. The company cares about automation, accuracy, and quality. Customers get good machines, help when needed, and custom choices for making aluminum foil.